Introduction of ‘C’
What is C?
C is a general-purpose programming language created by Dennis
Ritchie at the Bell Laboratories in 1972.
It is a very popular language, despite being old. The main reason
for its popularity is because it is a fundamental language in the field of
computer science.
C is strongly associated with UNIX, as it was developed to write
the UNIX operating system.
C एक
सामान्य-उद्देश्यीय प्रोग्रामिं language है जिसे 1972 में बेल लेबोरेटरीज में
डेनिस रिची द्वारा बनाया गया था।
पुरानी होने के बावजूद यह बहुत लोकप्रिय language है। इसकी लोकप्रियता का मुख्य कारण यह है कि यह कंप्यूटर science के क्षेत्र में एक fundamental
language है।
C, UNIX के साथ जुड़ा हुआ है, क्योंकि इसे UNIX ऑपरेटिंग सिस्टम लिखने के लिए
विकसित किया गया था।
Why Learn C? C क्यो सिखे?
- It
is one of the most popular programming language in the world
- If
you know C, you will have no problem learning other popular programming
languages such as Java, Python, C++, C#, etc, as the syntax is similar
- C
is very fast, compared to other programming languages, like Java and Python
- C
is very versatile; it can be used in both applications and technologies
• यह
दुनिया की सबसे लोकप्रिय प्रोग्रामिंग language में से एक है
• यदि आप ‘C’ जानते
हैं, तो आपको अन्य लोकप्रिय प्रोग्रामिंग language जैसे java, python, C++, C# आदि को
सीखने में कोई समस्या नहीं होगी, क्योंकि Syntax समान
है।
• java और python जैसी
अन्य प्रोग्रामिंग language की
तुलना में C बहुत fast है
• C का
उपयोग application और technologies दोनों
में किया जा सकता है
Difference between C and C++ (C और C++ मे अंतर)
- C++ was
developed as an extension of C, and both languages have almost the same
syntax
- The
main difference between C and C++ is that C++ support classes and objects,
while C does not
• C++ को C के advance के रूप
में develop किया
गया था, और दोनों भाषाओं का syntax लगभग समान है
• C और C++ के बीच
मुख्य अंतर यह है कि C++ class और object का support करता
है, जबकि C नहीं करता है
C Get Started (C को शुरु करे)
Get Started
With C
To start using C, you need two things:
- A
text editor, like Notepad, to write C code
- A
compiler, like GCC, to translate the C code into a language that the
computer will understand
There are many text editors and compilers to choose from. In this
tutorial, we will use an IDE (see
below).
C का
उपयोग शुरू करने के लिए, आपको
दो चीज़ों की आवश्यकता है:
• C कोड लिखने के लिए notepad जैसा एक text editor
• एक compiler जैसा GCC, C कोड को ऐसी भाषा में translate करने के लिए जिसे कंप्यूटर समझ सके
चुनने
के लिए कई टेक्स्ट editor और compiler उपलब्ध हैं।
C Install IDE (C के IDE को Install
An IDE (Integrated Development Environment) is used to edit AND
compile the code.
Popular IDE's include Code::Blocks, Eclipse, and Visual Studio.
These are all free, and they can be used to both edit and debug C code.
Note: Web-based IDE's can work as well, but
functionality is limited.
We will use Code::Blocks in
our tutorial, which we believe is a good place to start.
You can find the latest version of Code::Blocks at http://www.codeblocks.org/.
Download the mingw-setup.exe file, which will install
the text editor with a compiler.
C code को edit और compile करने के लिए एक IDE (Integrated Development Environment) का उपयोग किया जाता है।
Popular IDE में Code::Blocks, Eclipse और Visual Studio शामिल हैं। ये सभी free हैं, और इनका उपयोग C code को edit और debug करने दोनों के लिए किया जा सकता है।
नोट: Web-आधारित IDE भी काम कर सकता है, लेकिन functionality सीमित है।
हम अपने ट्यूटोरियल में Code::Blocks का उपयोग करेंगे, जिसके बारे में हमारा मानना
है कि शुरुआत करने के लिए यह एक अच्छी जगह है।
आप Code::Blocks का नवीनतम संस्करण http://www.codeblocks.org/
पर पा
सकते हैं। Mingw-setup.exe फ़ाइल डाउनलोड करें, जो कंपाइलर के साथ टेक्स्ट
एडिटर इंस्टॉल करेगी।
C Quickstart
Let's create our first C file.
Open Codeblocks and go to File > New > Empty File.
Write the following C code and save the file as myfirstprogram.c (File > Save File as):
आइए अपनी पहली C फ़ाइल बनाएं।
Code::Blocks खोलें और File > New > Empty File पर जाएँ।
निम्नलिखित
C कोड
लिखें और फ़ाइल को myfirstprogram.c के नाम से save (File > Save File as) करें:
myfirstprogram.c
#include
<stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("Hello
World!");
return 0;
}
Don't worry if you don't understand the code above - we will
discuss it in detail in later chapters. For now, focus on how to run the code.
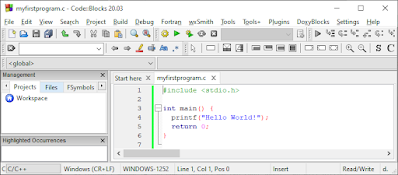
In Code::Blocks, it should look like this:
यदि आप उपरोक्त कोड को नहीं समझते हैं तो चिंता न करें - हम बाद के
अध्यायों में इस पर विस्तार से चर्चा करेंगे। अभी के लिए, कोड को चलाने के तरीके पर
ध्यान केंद्रित करें।
Code::Blocks में, इसे इस
तरह दिखना चाहिए:
Then, go to Build > Build and Run to run (execute) the program. The result will look something to this:
फिर, प्रोग्राम को execute (निष्पादित) करने के लिए Build > Build and Run पर जाएं। Output कुछ इस प्रकार दिखेगा:
Hello World!
Process
returned 0 (0x0) execution time : 0.011 s
Press any
key to continue.
Congratulations! You have now written and
executed your first C program.
Now let us explain the Example
#include
<stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("Hello
World!");
return 0;
}
Example
explained
Line 1: #include <stdio.h> is
a header file
library that lets us work with input and output functions,
such as printf() (used in line 4). Header files add
functionality to C programs.
Don't worry if you don't understand how #include
<stdio.h> works. Just think of it as something that (almost) always
appears in your program.
Line 2: A blank line. C ignores white space.
But we use it to make the code more readable.
Line 3: Another thing that always appears in
a C program is main(). This is called a function. Any code
inside its curly brackets {} will be executed.
Line 4: printf() is
a function used
to output/print text to the screen. In our example it will output "Hello
World!".
Note that: Every C statement ends
with a semicolon (;)
Note: The body of int main() could
also been written as:
int
main(){printf("Hello World!");return 0;}
Remember: The compiler ignores white spaces.
However, multiple lines makes the code more readable.
Line 5: return 0 ends
the main() function.
Line 6: Do not forget to add the closing
curly bracket } to actually end the main function.
पंक्ति 1: #include <stdio.h> एक हेडर फ़ाइल लाइब्रेरी है जो हमें इनपुट और आउटपुट
फ़ंक्शंस, जैसे
कि printf() (पंक्ति 4 में
प्रयुक्त) के साथ काम करने देती है। हेडर फ़ाइलें C प्रोग्राम में कार्यक्षमता
जोड़ती हैं।
यदि आप यह नहीं समझते कि #include <stdio.h> कैसे काम करता है, तो चिंता न करें। बस इसे कुछ
ऐसा समझें जो (लगभग) हमेशा आपके प्रोग्राम में दिखाई देता है।
पंक्ति 2: एक
रिक्त पंक्ति. C language white space को नजरअंदाज
(ignore) करता
है। लेकिन हम इसका उपयोग कोड (code) को अधिक पठनीय (readable) बनाने के लिए करते हैं।
पंक्ति 3: एक और
चीज़ जो हमेशा C प्रोग्राम
में दिखाई देती है, वह है main()। इसे एक फ़ंक्शन कहा जाता
है. इसके curly braces {} के अंदर कोई भी code execute किया जाएगा।
पंक्ति 4: printf() एक फ़ंक्शन है जिसका उपयोग स्क्रीन पर text को output/print करने के लिए किया जाता है। हमारे उदाहरण में यह "
Hello World!" Output देगा।
ध्यान दें: प्रत्येक C statement semicolon (;) के साथ समाप्त होता है;
नोट: int main() का मुख्य भाग इस प्रकार भी लिखा जा सकता है:
int main(){printf('Hello
World');return 0;}
याद रखें: कंपाइलर white space को ignore करता है। हालाँकि, एकाधिक पंक्तियाँ कोड को अधिक
पठनीय बनाती हैं।
पंक्ति 5: return 0 main() function को समाप्त करता है।
पंक्ति
6: main function को वास्तव में समाप्त करने
के लिए closing curly bracket (}) जोड़ना न भूलें।
Output (Print Text)
To output values or print text in C, you can use the printf() function:
C में value या text प्रिंट करने के लिए, आप printf()
फ़ंक्शन
का उपयोग कर सकते हैं:
Example
#include
<stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("Hello
World!");
return 0;
}
You can use as many printf() functions
as you want. However,
note that it does not insert a new line at the end of the output:
आप
जितने चाहें उतने printf() फ़ंक्शंस का उपयोग कर सकते हैं। हालाँकि, ध्यान दें कि यह आउटपुट के
अंत में एक नई लाइन नहीं डालता है:
Example
#include
<stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("Hello
World!");
printf("I am learning C.");
return 0;
}
New Lines
To insert a new line, you can use the \n character:
नई line insert करने के लिए, आप \n character का उपयोग कर सकते हैं:
Example
#include
<stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("Hello
World!\n");
printf("I am learning C.");
return 0;
}
You can also output multiple lines with a single printf() function.
However, this could make the code harder to read:
आप एक
ही printf() फ़ंक्शन के साथ कई लाइनें भी आउटपुट कर सकते हैं। हालाँकि, इससे कोड को पढ़ना कठिन हो
सकता है:
Example
#include
<stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("Hello
World!\nI am
learning C.\nAnd
it is awesome!");
return 0;
}
Tip: Two \n characters
after each other will create a blank line:
एक के
बाद एक दो \n अक्षर
एक रिक्त रेखा बनाएंगे
Example
#include
<stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("Hello
World!\n\n");
printf("I am learning C.");
return 0;
}
What
is \n exactly?
The newline character (\n) is called an escape sequence, and
it forces the cursor to change its position to the beginning of the next line
on the screen. This results in a new line.
Examples of other valid escape sequences are:
newline character (\n) को escape sequence कहा जाता है, और यह cursor को screen पर अगली लाइन की शुरुआत में रखने
के लिए मजबूर करता है। इसके परिणामस्वरूप एक नई लाइन बनती है.
अन्य valid escape sequence के उदाहरण हैं:
|
Escape Sequence |
Description |
|
\t |
Creates a horizontal tab |
|
\\ |
Inserts a backslash character (\) |
|
\" |
Inserts a double quote character |




No comments:
Post a Comment