Constructors
A constructor in C++ is a special method that is
automatically called when an object of a class is created.
To create a constructor, use the same name as the class, followed
by parentheses ():
C++ में constructor एक विशेष method है जिसे किसी class का object बनाते
समय automatically कॉल
किया जाता है।
कंस्ट्रक्टर बनाने के लिए, class के
समान नाम का उपयोग करें, उसके बाद कोष्ठक ():
Example
class MyClass { // The class
public: // Access specifier
MyClass()
{ //
Constructor
cout
<< "Hello
World!";
}
};
int main() {
MyClass myObj; // Create an object of MyClass (this will call the
constructor)
return 0;
}
Note: The constructor has the same name as
the class, it is always public, and
it does not have any return value.
constructor का नाम
class के
समान है, यह हमेशा public होता है, और इसका कोई return value नहीं
होता है।
Constructor Parameters
Constructors can also take parameters (just like regular
functions), which can be useful for setting initial values for attributes.
The following class have brand, model and year attributes, and a constructor with
different parameters. Inside the constructor we set the attributes equal to the
constructor parameters (brand=x, etc).
When we call the constructor (by creating an object of the class), we pass
parameters to the constructor, which will set the value of the corresponding
attributes to the same:
constructor parameter भी ले
सकते हैं (regular function की
तरह), जो attributes के लिए
initial value set करने
के लिए उपयोगी हो सकते हैं।
निम्नलिखित class में brand, model और year attributes और
विभिन्न parameter वाला
एक constructor है। constructor के
अंदर हम constructor parameter (brand = x, आदि) के
बराबर attributes set करते
हैं। जब हम constructor को call करते
हैं (class का object बनाकर), हम constructor को parameter पास
करते हैं, जो संबंधित attributes का value उसी पर set करेगा:
Example
class Car
{ // The class
public: // Access specifier
string
brand; //
Attribute
string model; // Attribute
int year; // Attribute
Car(string x, string
y, int z) { // Constructor with parameters
brand
= x;
model = y;
year = z;
}
};
int main() {
//
Create Car objects and call the constructor with different values
Car carObj1("BMW", "X5", 1999);
Car carObj2("Ford", "Mustang", 1969);
//
Print values
cout << carObj1.brand << " " << carObj1.model << " " << carObj1.year << "\n";
cout << carObj2.brand << " " << carObj2.model << " " << carObj2.year << "\n";
return 0;
}
Just like functions, constructors can also be defined outside the
class. First, declare the constructor inside the class, and then define it
outside of the class by specifying the name of the class, followed by the scope
resolution operator(::), followed by the name of the constructor (which is
the same as the class):
Function की तरह, constructor को भी class के
बाहर define किया
जा सकता है। सबसे पहले, constructor को class के
अंदर declare करें, और फिर class के नाम
को specify करके
इसे class के
बाहर define करें, उसके
बाद scope resolution operator (::), उसके
बाद constructor का नाम
(जो कि class के
समान है) specify करें।
:
Example
class Car
{ // The class
public: // Access specifier
string brand; // Attribute
string
model; //
Attribute
int year; // Attribute
Car(string x, string
y, int z); //
Constructor declaration
};
// Constructor definition outside the class
Car::Car(string x, string y, int z)
{
brand = x;
model = y;
year = z;
}
int main() {
//
Create Car objects and call the constructor with different values
Car carObj1("BMW", "X5", 1999);
Car carObj2("Ford", "Mustang", 1969);
//
Print values
cout << carObj1.brand << " " << carObj1.model << " " << carObj1.year << "\n";
cout << carObj2.brand << " " << carObj2.model << " " << carObj2.year << "\n";
return 0;
}
Copy
Constructor
The copy constructor is a
constructor which creates an object by initializing it with an object of the
same class, which has been created previously. The copy constructor is used to:
·
Initialize one object from another of the same type.
·
Copy an object to pass it as an argument to a function.
·
Copy an object to return it from a function.
If a copy constructor is not defined in a class, the compiler itself
defines one. If the class has pointer variables and has some dynamic memory
allocations, then it is must to have a copy constructor. The most common form
of copy constructor is shown here:
Copy constructor एक constructor है जो किसी object को उसी class के object से initialize करके बनाता है, जो पहले बनाया गया है। copy constructor का उपयोग इसके लिए किया
जाता है:
• एक ही प्रकार की
दूसरी object से initialize।
• किसी object को function में logic के रूप में पास करने के लिए
उसे copy करें।
• किसी object को किसी function से return करने के लिए उसे copy करें।
यदि किसी class में copy constructor को define नहीं किया गया है, तो compiler स्वयं उसे define करता है। यदि class में pointer variables हैं और कुछ dynamic memory allocation हैं, तो एक copy constructor का होना आवश्यक है। copy constructor का सबसे common form यहां दिखाया गया है:
Here, obj is a reference to an object that is
being used to initialize another object.
यहां, obj एक object का reference है जिसका उपयोग किसी अन्य object को initialize करने के लिए किया जा रहा
है।
Q WAP using copy
constructor?
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Furniture
{
int price;
public:
Furniture(int x)
{
price=x;
}
Furniture(const
Furniture &obj)
{
price=obj.price;
}
void getdata()
{
cout<<"Price is="<<price<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Furniture f1(7000);
f1.getdata();
Furniture f2(f1);
f2.getdata();
Furniture f3(0);
f3=f1;
f3.getdata();
}
Q WAP using copy constructor, pointer, dynamic memory allocation
etc?
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Line
{
private:
int *ptr,length;
public:
int getLength( void );
Line( int len ); //parameterised
constructor
Line( const Line &obj); //
copy constructor
~Line(); // destructor
};
// Member functions definitions including constructor
Line::Line(int len)
{
cout << "Normal constructor allocating ptr"
<< endl;
// allocate memory for the pointer;
//ptr = new int;
//*ptr = len;
length=len;
ptr=&length;
}
Line::Line(const Line &obj)
{
cout << "Copy constructor allocating ptr."
<< endl;
ptr = new int;
*ptr = *obj.ptr; // copy the value
}
Line::~Line(void)
{
cout << "Freeing memory!" << endl;
delete ptr;
}
int Line::getLength( void )
{
return *ptr;
}
void display(Line obj)
{
cout << "Length of line : " <<
obj.getLength() <<endl;
}
// Main function for the program
int main( )
{
Line line(10);
display(line);
int x=line.getLength();
cout<<"Length="<<x;
Line line2=line;
int y=line2.getLength();
cout<<"length
of line2:"<<y;
return 0;
}
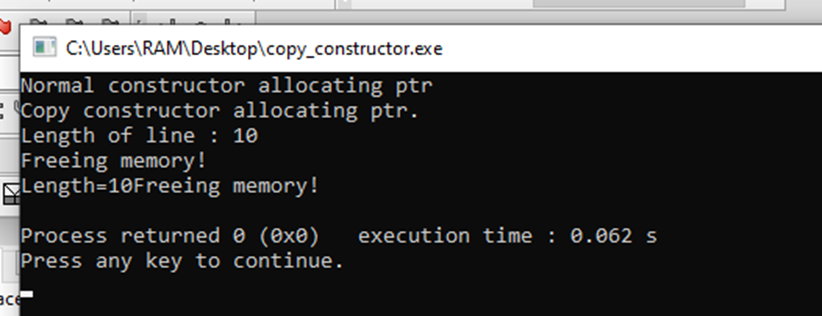
Output is
Q WAP using copy constructor, pointer, dynamic memory allocation etc?
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Line
{
private:
int *ptr;
public:
int getLength( void );
Line( int len ); //parameterised
constructor
Line( const Line &obj); //
copy constructor
~Line(); // destructor
};
// Member functions definitions including constructor
Line::Line(int len)
{
cout << "Normal constructor allocating ptr"
<< endl;
// allocate memory for the pointer;
ptr = new int;
*ptr = len;
}
Line::Line(const Line &obj)
{
cout << "Copy constructor allocating ptr."
<< endl;
ptr = new int;
*ptr = *obj.ptr; // copy the value
}
Line::~Line(void)
{
cout << "Freeing memory!" << endl;
delete ptr;
}
int Line::getLength( void )
{
return *ptr;
}
void display(Line obj)
{
cout << "Length of line : " <<
obj.getLength() <<endl;
}
// Main function for the program
int main( )
{
Line line(10);
display(line);
int x=line.getLength();
cout<<"Length="<<x;
return 0;
}
Output is






No comments:
Post a Comment